Quantum Computing: The new ambiguous technology emerging in the world
Quantum computing is an emerging field that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as the smallest unit of data (represented as 0s and 1s), quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits. Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to the phenomena of superposition and entanglement, allowing quantum computers to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds.
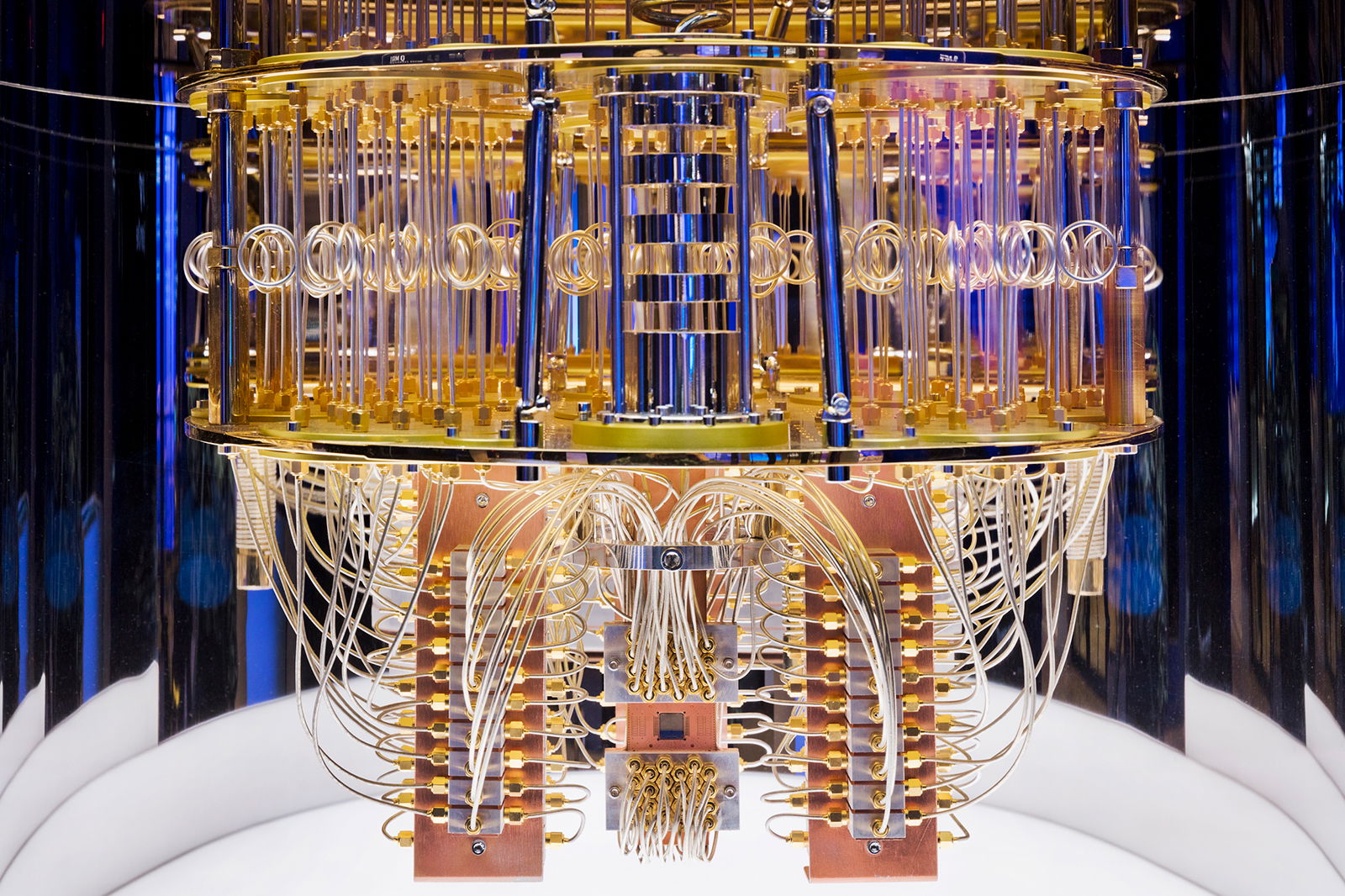
(Fingas 2021)
At the heart of quantum computing is the quantum process, which leverages superposition and entanglement to solve problems. Superposition allows qubits to be in multiple states at once, rather than being limited to a single binary state like classical bits. This enables quantum computers to process a vast number of possibilities simultaneously. Entanglement, another key quantum principle, allows qubits that are entangled to be instantaneously correlated, no matter the distance between them. This interconnectedness can be used to transfer information and perform calculations much faster than classical systems.
The potential applications of quantum computing are vast and transformative. In cryptography, quantum computers could break current encryption methods by efficiently factoring large numbers, which is a cornerstone of many cryptographic systems. However, they also hold the promise of creating new, virtually unbreakable encryption techniques. In materials science, quantum computing could accelerate the discovery of new materials by simulating atomic and molecular interactions with high precision. This could lead to breakthroughs in industries such as pharmaceuticals, where drug discovery and molecular modeling could be revolutionized. Additionally, quantum computing could optimize complex systems in fields like logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence, solving problems that are currently infeasible for classical computers.
Despite its immense potential, quantum computing is still in its infancy. Challenges such as qubit stability, error rates, and the need for extremely low temperatures to maintain quantum states remain significant hurdles. However, research and development are progressing rapidly, with companies like IBM, Google, and Microsoft making strides toward practical quantum computing.In summary, quantum computing represents a paradigm shift in how we process information. By exploiting the unique properties of quantum mechanics, it offers the possibility of solving problems that were once thought to be unsolvable. As the field advances, quantum computing is poised to revolutionize industries and redefine the limits of what technology can achieve.
Image: Fingas, J. (2021, February 4) IBM quantum computers now finish some tasks in hours, not months. Engadget.